What is Fault Tree analysis in Health and Safety? Is
Fault tree analysis a Qualitative or Quantitative Risk assessment?
Risk assessment is of two type .i.e. Quantitative and
Qualitative. Quantitative risk assessment means prioritizing the risk through its
quantification. Like in 5 X 5 risk assessment matrix, risk prioritized on the
basis of Severity and Probability. We multiply both severity and probability
and higher the number higher the risk. This ranking or numbering gives us an
idea about dealing the high number risk prior to low number risk. This is
called as Quantitative risk assessment and Fault tree analysis is one of the
quantitative risk assessment techniques as well as qualitative too.
Qualitative risk assessment means no quantity and hazard,
risk identified from the activity. After identification of hazard and risk we
apply control. There is no priority, no ranking. This is called as qualitative
risk assessment. Example of qualitative risk assessment is Job safety analysis
(JSA).
Fault Tree analysis
Facts about Fault tree analysis are as below:
1-
Regularly used technique in High hazard
industries like Chemical, aerospace, nuclear power station.
2-
Top down based
3-
Deductive failure analysis
4-
Mathematical technique used for large and
complex processes.
5-
Based on Boolean algebra (Use of 0 and 1)
Steps to perform an event tree analysis:
Define the system:
Define what needs to be involved or where to draw the boundaries.
Identify the accident
scenarios: Perform a system assessment to find hazards or accident
scenarios within the system design.
Identify the basic
events: Basic events are at bottom of the graphical representation, here
basic events mentioned in the picture are failure of sprinkler system in case
of fire, fail to call Fire department etc..
Identify Top events:
Graphically represent top event interacting to cause total loss. Like here we
mentioned in the picture Fire as a Top event.
Obtain event failure
probabilities: If the failure probability can be obtained by use of fault
tree analysis.
Document the FTA:
Document the entire process on the Fault tree diagrams and update for new
information as needed.
Advantages:
Fault tree analysis can be used to:
1-
Understand the logic leading to the top event /
undesired state.
2-
Show compliance with the (input) system safety /
reliability requirements.
3-
Prioritize the contributors leading to the top
event - Creating the Critical Equipment/Parts/Events lists for different
importance measures.
4-
Monitor and control the safety performance of
the complex system (e.g., is a particular aircraft safe to fly when fuel valve
x malfunctions? For how long is it allowed to fly with the valve malfunction?).
5-
Minimize and optimize resources.
6-
Assist in designing a system. The FTA can be
used as a design tool that helps to create (output / lower level) requirements.
7-
Function as a diagnostic tool to identify and
correct causes of the top event. It can help with the creation of diagnostic
manuals / processes.
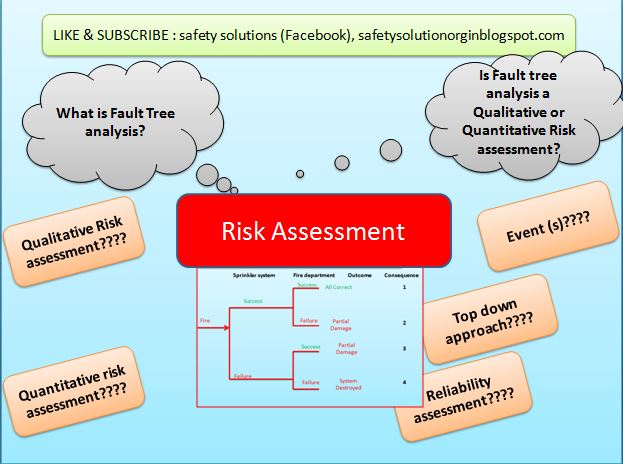
Example:
In the below given picture we have considered Top event as “Fire”
Qualitative Fault tree diagram suggest below things:
1-
Consequence 1- Fire happens and in case
Sprinkler work and fire department called then “No” damage happened.
2-
Consequence 2- Fire happens and Sprinkler worked
but didn’t called fire department or didn’t called on time the Partial damage
may happen.
3-
Consequence 3- Fire happens and sprinkler not
worked but fire department called then also Partial damage may happen.
4-
Consequence 4- Fire happens and both function
not worked. Sprinkler not worked and Fire department not called then Total
system destroyed damage happen.







Hi there! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I really enjoy reading through your articles. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that go over the same subjects? Thanks! safety decking systems
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteGreat article on event tree analysis! For those in need of professional tree care services, Betzy’s Tree Care offers expert tree risk assessments Sacramento
ReplyDelete, ensuring the safety of your property. Highly recommend their services for accurate, reliable assessments!